See here for Business Tax Deadlines
Any person who receives an income in South Africa has to be registered for tax purposes with SARS. A person resident in South Africa is taxed on their worldwide income while non-residents are taxed only on their income that has its source within South Africa. However, in terms of new legislation effective from 1 March 2020, South African residents who work abroad, and as a result do not fall into the “tax” definition of a South African resident, will be taxed on any foreign employment income that exceeds R1 million (double taxation arrangements apply).
Personal income tax is based on a person’s taxable income according to a tax table which incorporates a sliding scale.
The taxable income is then reduced by age related rebates. In practical terms taxable income is derived by reducing income with items that are allowed for tax purposes (if any) and adding taxable capital gains (if any). A capital gain arises from the disposal of certain assets when the proceeds exceed the cost, and the taxable portion needs to be specially calculated.
Any company doing business in South Africa that employs people must register with SARS and should have a tax number for all employees.
Employers are required to deduct PAYE from employee’s salaries and wages and pay them over to SARS. The PAYE paid is taken into account when the employees tax for that tax year is assessed (the tax certificates submitted by the employer are captured on the SARS data base for each tax payer).
Employees who earn less than R350,000 pa. for a full year from one employer, have no other sources of income and don’t want to claim any deductions, do not have to submit a tax return.
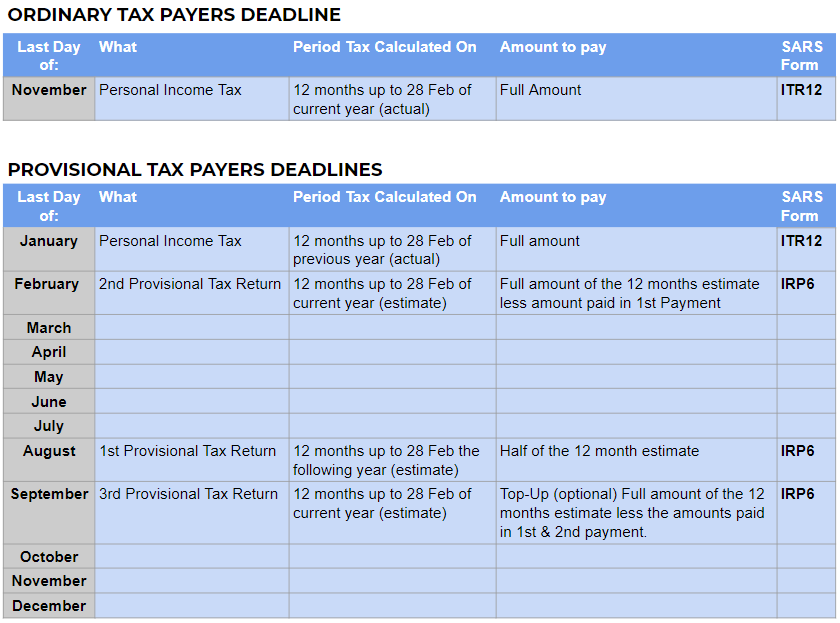
If a person earns income other than a salary or an allowance they must register as a provisional tax payer. A sole proprietor and a partner are taxed as individuals and must include their business profits in the relevant section of their personal tax returns. They must also register as provisional taxpayers. Provisional tax payers often do not have PAYE deducted and are required to pay taxes in advance. They need to file two returns (IRP6’s) and pay two amounts in advance during the year, based on estimated taxable income. A third provisional tax return (IRP6) for a top-up payment is optional.
It is recommended that all tax payers should register with SARS eFiling (www.sarsefiling.gov.za) where their income tax return (ITR 12) and provisional tax returns (IRP6’s) are generated for them and can be submitted online. Alternatively, they can appoint a tax practitioner who can handle their taxes on eFiling for them and ensure that they claim all of what is allowable.
Tax returns (ITR12) must be filed by 30 November for the year of assessment ending the previous February.
See also: Business Income Tax Guide - South Africa